User Guide
SETA is a desktop application for CS2103T Teaching Assistants to track their students’ and tutorials’ details, and questions asked by students. SETA is optimized for use via a Command Line Interface (CLI) while still having the benefits of a Graphical User Interface (GUI). If you can type fast, SETA enables you to track your students. manage your tutorials and note down questions more effectively than traditional GUI apps.
- Table of Contents
- Quick Start
-
Features
-
Students
- Adding a student:
addstu - Editing a student:
editstu - Adding student’s attendance:
attendance - Adding student’s response:
addresponse - Adding help tag to a student:
helpstu - Removing help tag from a student:
unhelpstu - Deleting a student:
deletestu - Finding a student:
findstu - Listing all students:
liststu
- Adding a student:
- Questions
- Tutorials
-
Clear:
clear -
Exiting the program:
exit
-
Students
- FAQ
- Command Summary
Quick Start
-
Ensure you have Java
11or above installed in your Computer. -
Download the latest
SETA.jarfrom here. -
Copy the file to the folder you want to use as the home folder for your SETA.
- Double-click the file to start the app.
- If double-clicking does not work, you can go to the directory containing the SETA.jar file through your terminal
and run
java -jar SETA.jarto launch the application.
- If double-clicking does not work, you can go to the directory containing the SETA.jar file through your terminal
and run
-
The GUI similar to the below should appear in a few seconds. Note how the app contains some sample data.
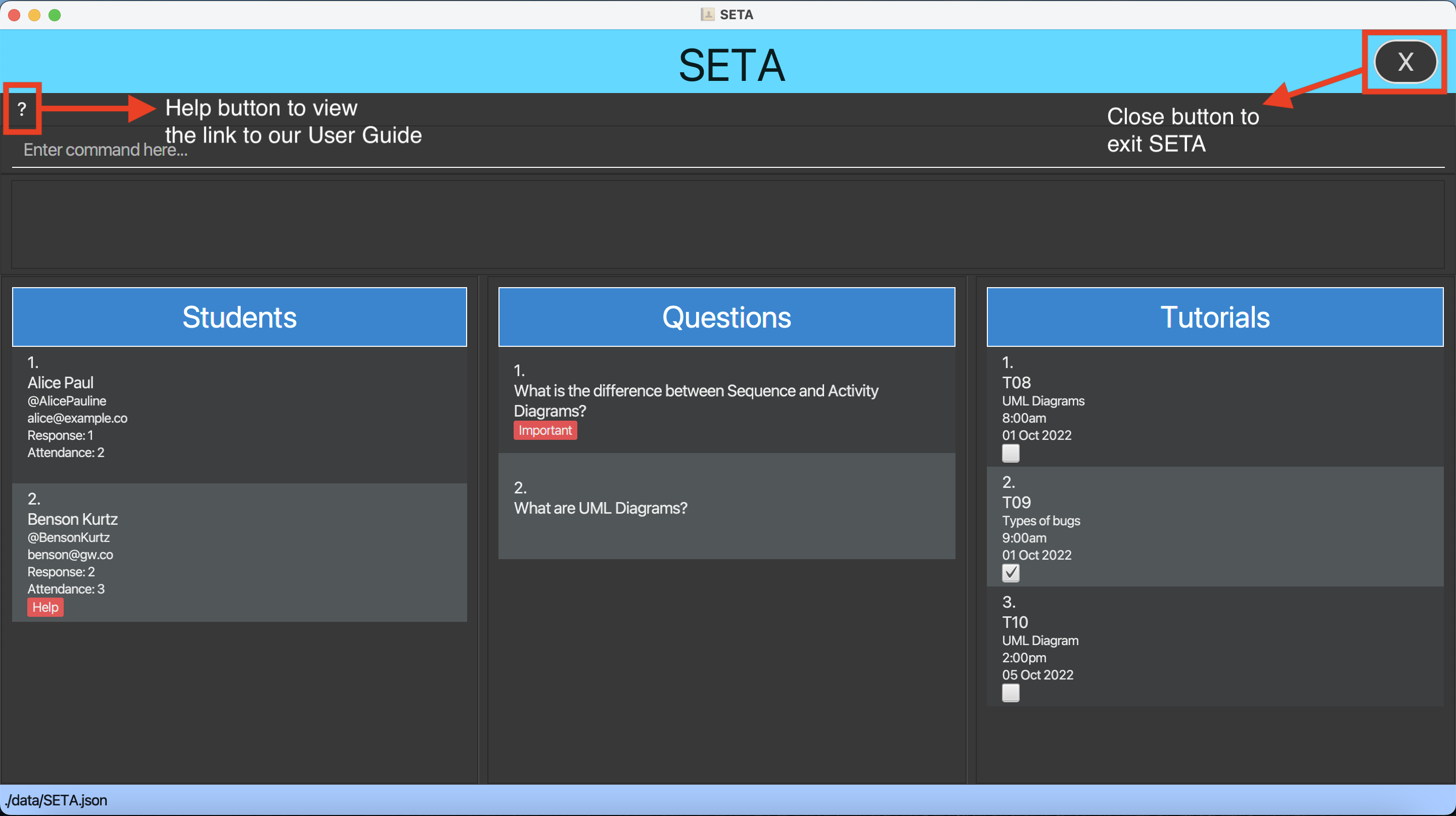
- Type the command in the command box and press Enter to execute it. e.g. typing
liststuand pressing Enter will list all the students in the ‘Student’ column.
Some example commands you can try:
-
addstun/John Lim Jun Jie h/@johnlimjj e/johnlim@example.com: Adds a student namedJohn Lim Jun Jieto the student list. -
deletestu3: Deletes the 3rd student shown in the current list. -
exit: Exits the app.
- Refer to the Features below for details of each command.
Features
![]() Notes about the command format:
Notes about the command format:
-
Words in
UPPER_CASEare the parameters to be supplied by the user.
e.g. inaddstu n/NAME,NAMEis a parameter which can be used asaddstu n/John Lim. -
Items in square brackets are optional.
e.g.n/NAME [h/TELEGRAM_HANDLE]can be used asn/John Lim h/@johnlimor asn/John Lim. -
Parameters can be in any order.
e.g. if the command specifiesn/NAME e/EMAIL,e/EMAIL n/NAMEis also acceptable. -
If a parameter is expected only once in the command, but you specified it multiple times, only the last occurrence of the parameter will be taken.
e.g. if you specifyh/@johnlim h/@johnlimjj, onlyh/@johnlimjjwill be taken. -
Extraneous parameters for commands that do not take in parameters (such as
liststuandexit) will be ignored.
e.g. if the command specifiesliststu 123, it will be interpreted asliststu.
Students
Each student contains details such as their name, telegram handle and email. The latter two are there for you to contact the student if necessary. You can also track each student’s attendance and include the number of messages he has sent on Zoom to note down his participation.
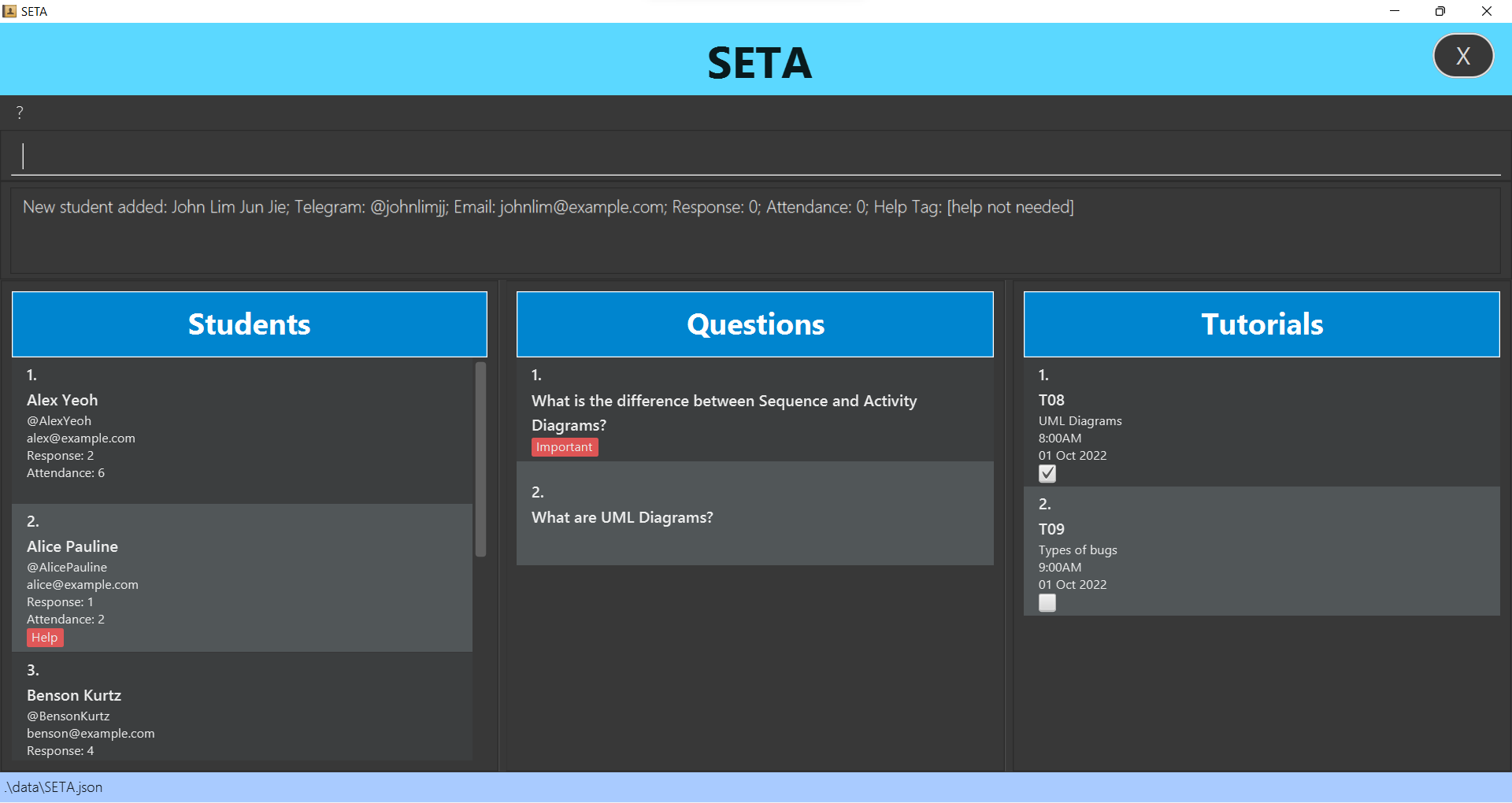
Adding a student : addstu
Adds a student to the student list.
Format: addstu n/NAME h/TELEGRAM_HANDLE e/EMAIL
- Telegram handle must start with a ‘@’, followed by an alphanumeric character.
- After the first character, telegram handle can only contain alphanumeric character or underscore.
- Email can only contain alphanumeric characters and must contain a top level domain with at least 2 characters
(E.g. of top level domain:
.com,.co,.edu).
Examples:
addstu n/John Lim Jun Jie h/@johnlimjj e/johnlim@example.comaddstu n/Mary Tan Xiao Li h/@marytxl e/marytxl@example.edu
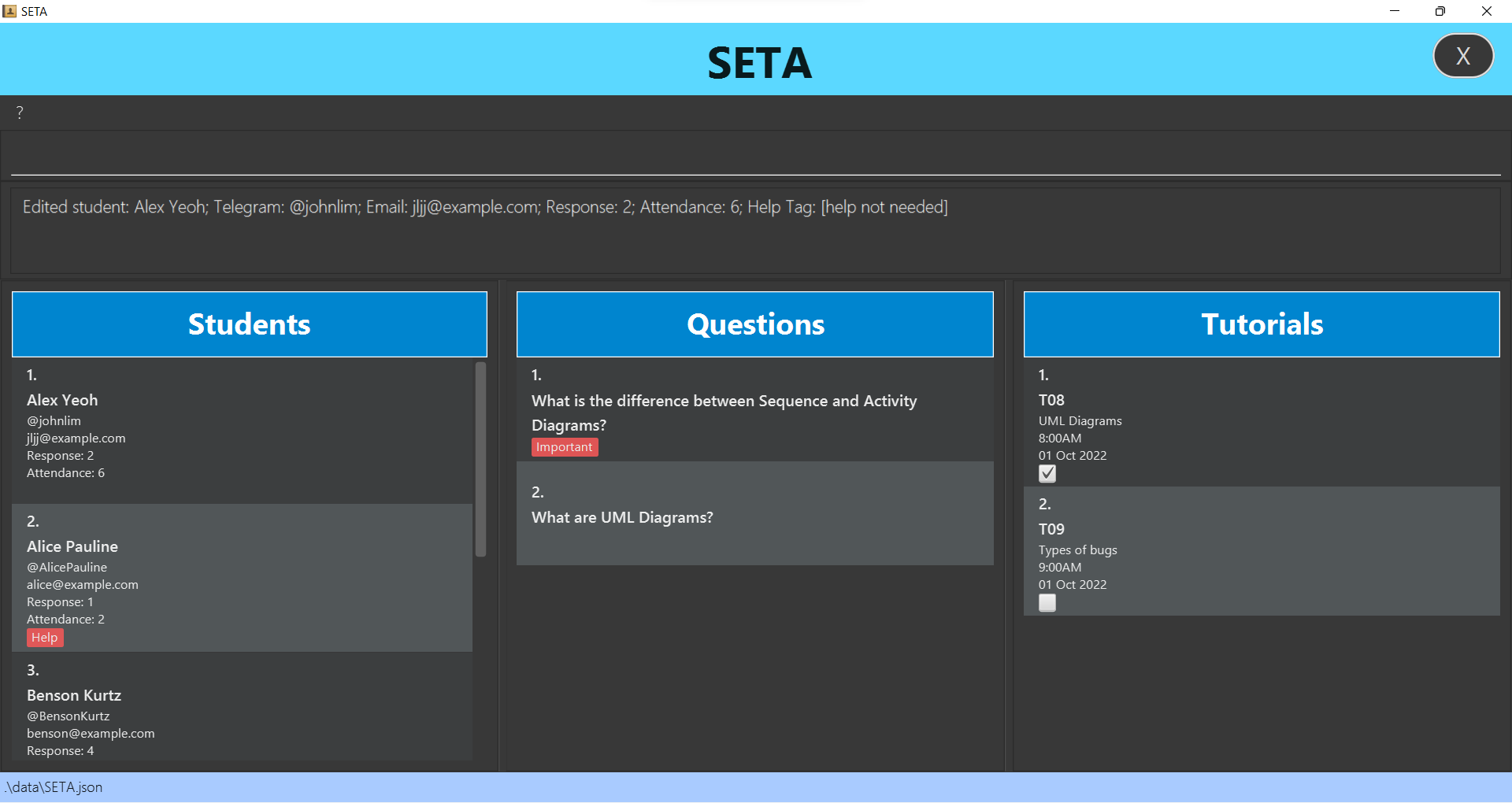
Editing a student: editstu
Edits an existing student in the student list.
Format: editstu INDEX [n/NAME] [h/TELEGRAM_HANDLE] [e/EMAIL] [a/ATTENDANCE]
- Edits the student at the specified INDEX. The index represents the index number of the student in the student list. The index must be a positive integer 1, 2, 3…
- At least one of the fields (E.g. [n/NAME] or [e/EMAIL]) must be provided.
- Existing fields will be updated to the input values.
- Editing a student with the same details as the student’s original details will be accepted.
(E.g. executing
editstu 1 h/@testwhen student 1’s telegram handle is already@test, will still be accepted as an edit.) - Input attendance value without any extra ‘0’s before and after the intended attendance value. (E.g. ‘0’ instead of ‘ 0000’ and ‘3’ instead of ‘003’).
Examples:
-
editstu 1 h/@johnlim e/jljj@example.comEdits the telegram handle and email of the 1st student to @johnlim and jljj@example.com respectively. -
editstu 3 n/Mary Lee Jing YiEdits the name of the 3rd student to Mary Lee Jing Yi. -
editstu 2 a/5Edits the attendance number of the 2nd student to 5.
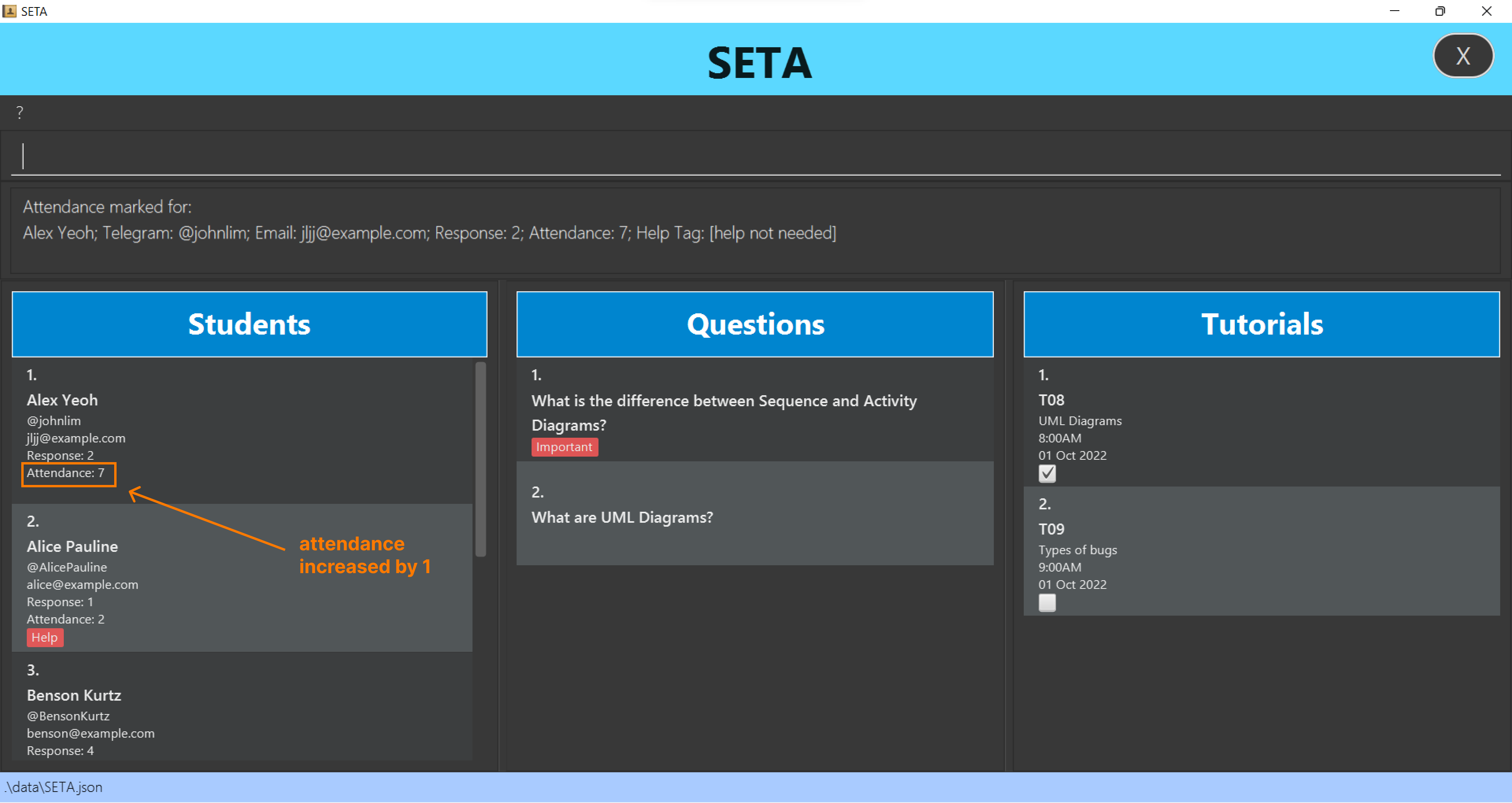
Adding student’s attendance : attendance
Increases student’s attendance by 1.
Format: attendance INDEX
- Increment attendance to the student at the specified INDEX.
- The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed student list.
- The index must be a positive integer 1, 2, 3…
Example:
attendance 1
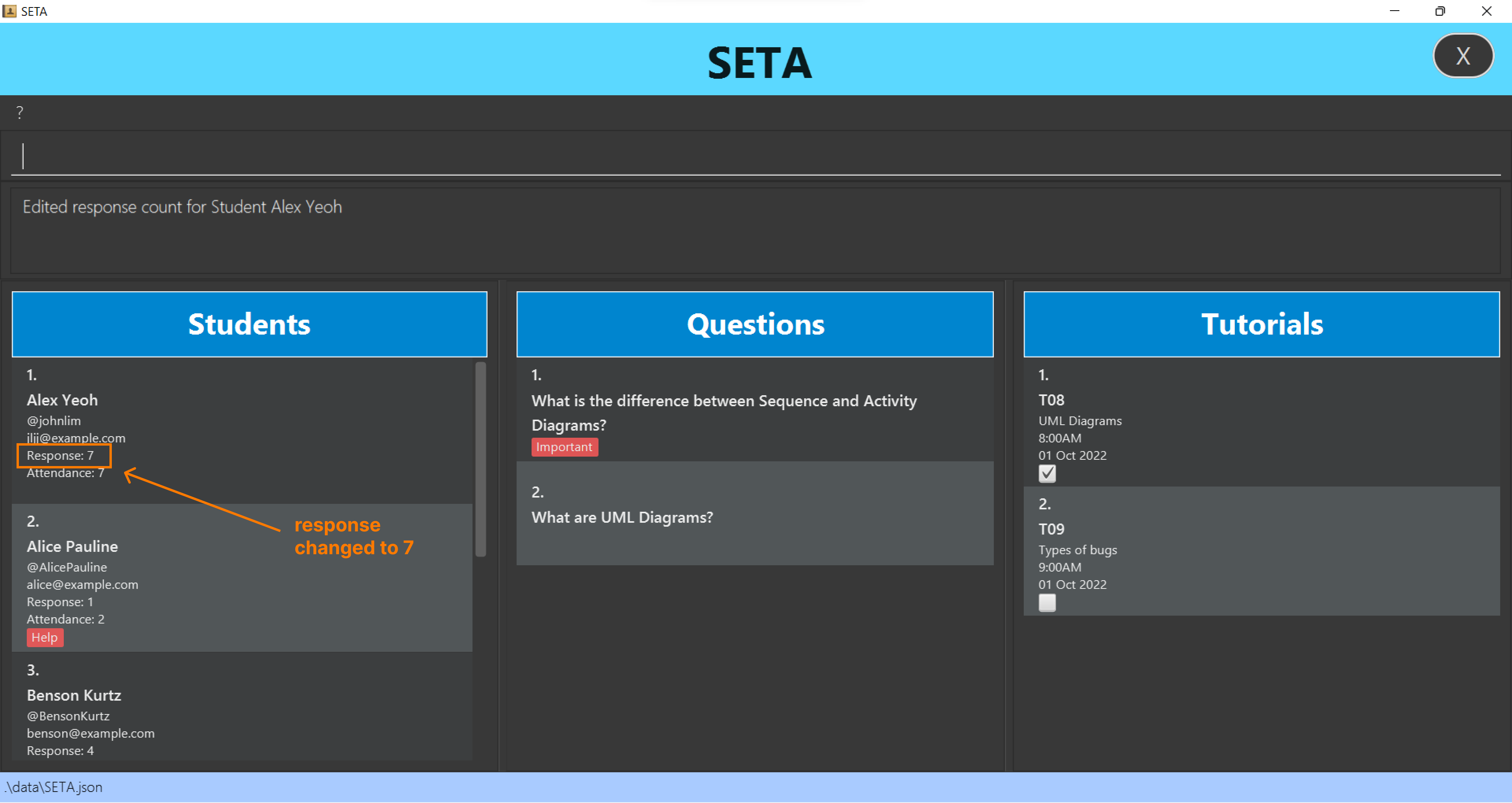
Adding student’s response: addresponse
Edits the number of messages a specified student sent during tutorial.
Format: addresponse INDEX m/MESSAGE_COUNT
- Edits response count of the student at the specified INDEX.
- If
addresponse 1 m/7is keyed in afteraddresponse 1 m/2, the response count for the first student in the student list will be 7 instead of 2.
- If
- The
INDEXrefers to the index number shown in the displayed student list. - The
INDEXmust be a positive integer 1, 2, 3… - The
MESSAGE_COUNTmust be a positive integer 1, 2, 3… - If
m\0000000000is given as an input, 0s will not be truncated and response will be displayed asresponse: 000000000
Example:
addresponse 1 m/7
Adding help tag: helpstu
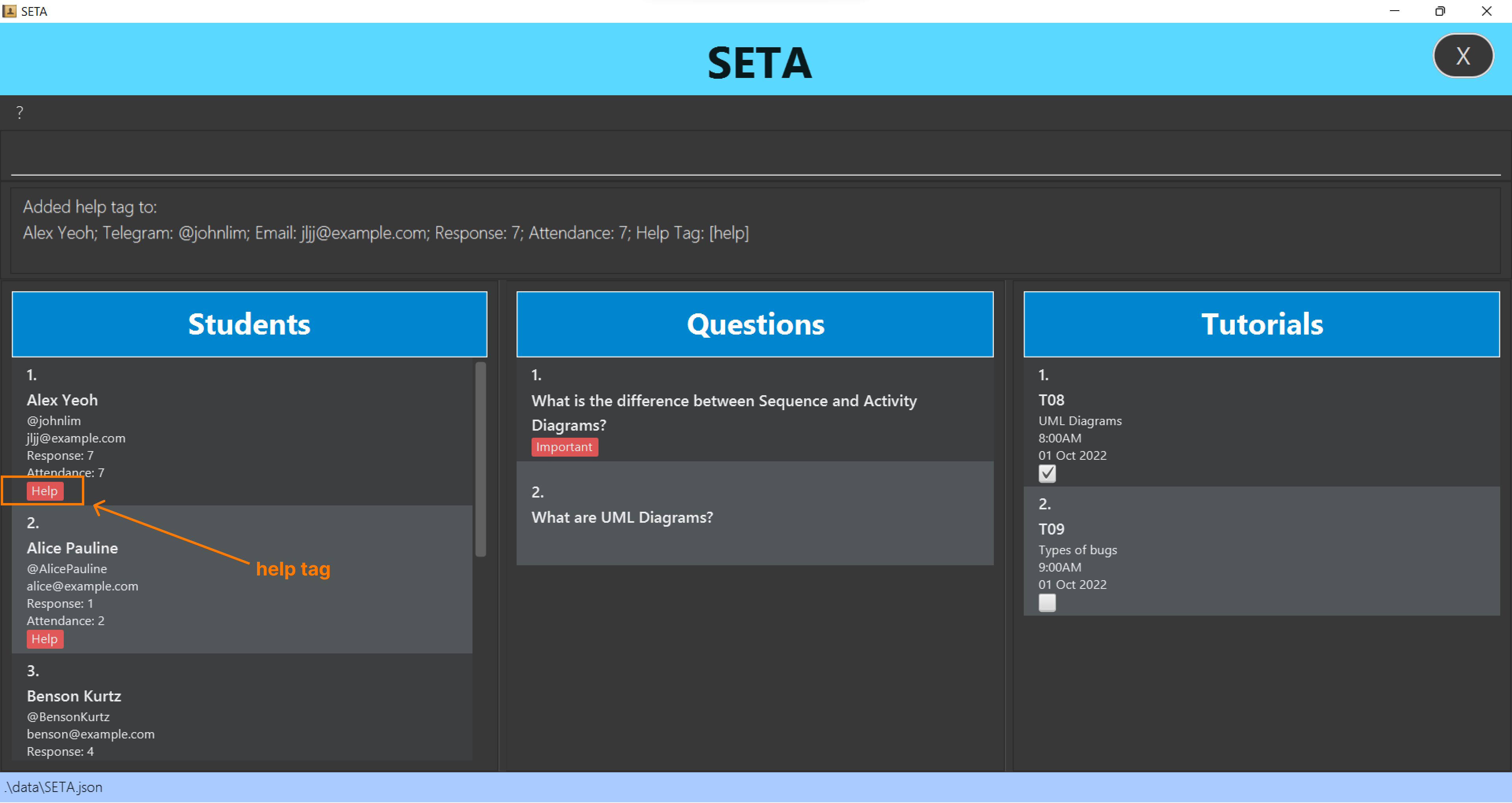
Adds a help tag to an existing student.
Format: helpstu INDEX
- Adds a help tag to the student at the specified INDEX.
- The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed student list.
- The index must be a positive integer 1, 2. 3…
- Adding help tag to a student who is already tagged with help tag will not change anything.
Example:
helpstu 1
Removing help tag: unhelpstu
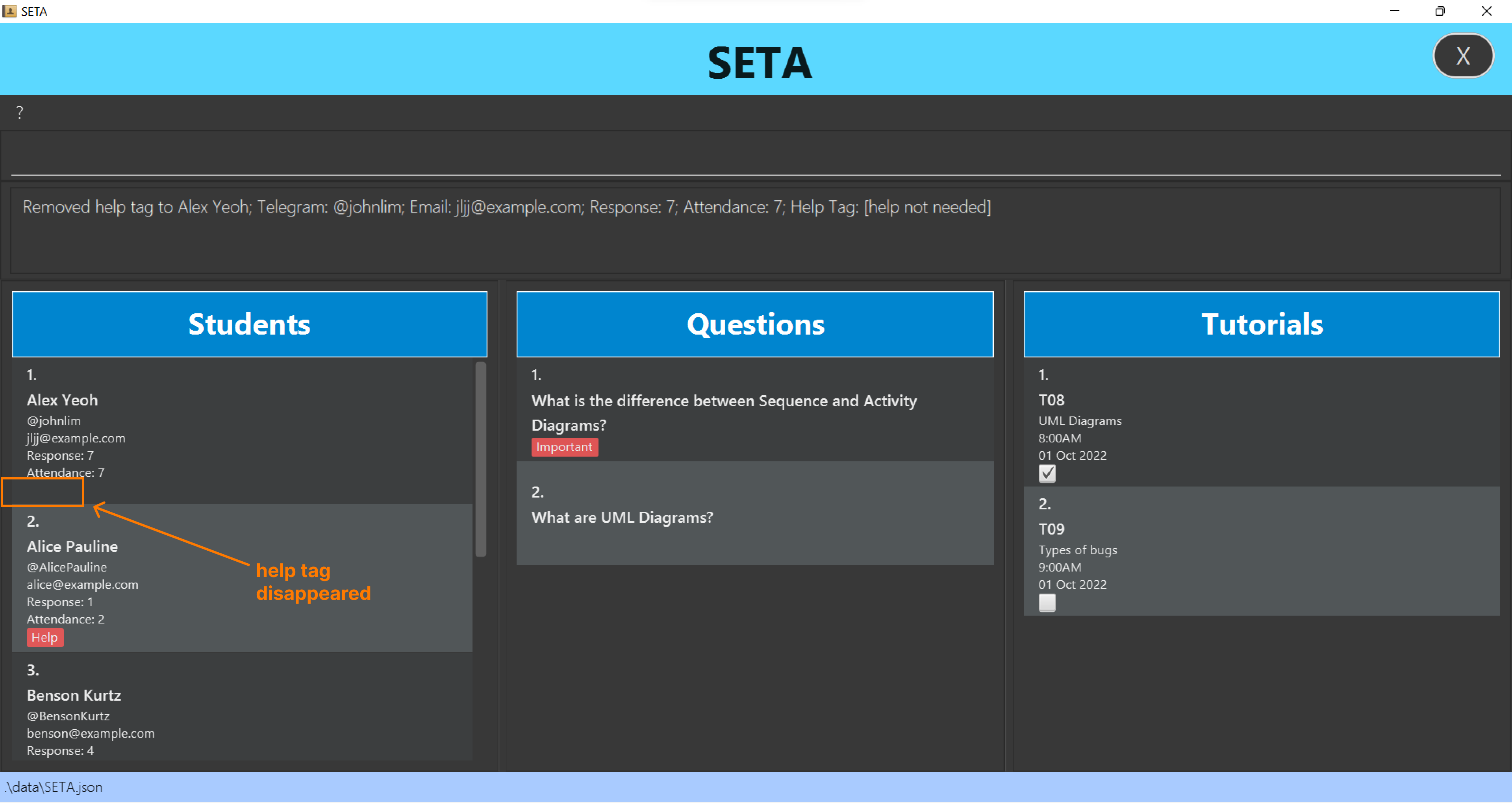
Removes help tag from an existing student.
Format: unhelpstu INDEX
- Removes help tag to the student at the specified INDEX.
- The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed student list.
- The index must be a positive integer 1, 2. 3…
- Removing help tag from a student who does not have a help tag will not change anything.
Example:
unhelpstu 1
Deleting a student: deletestu
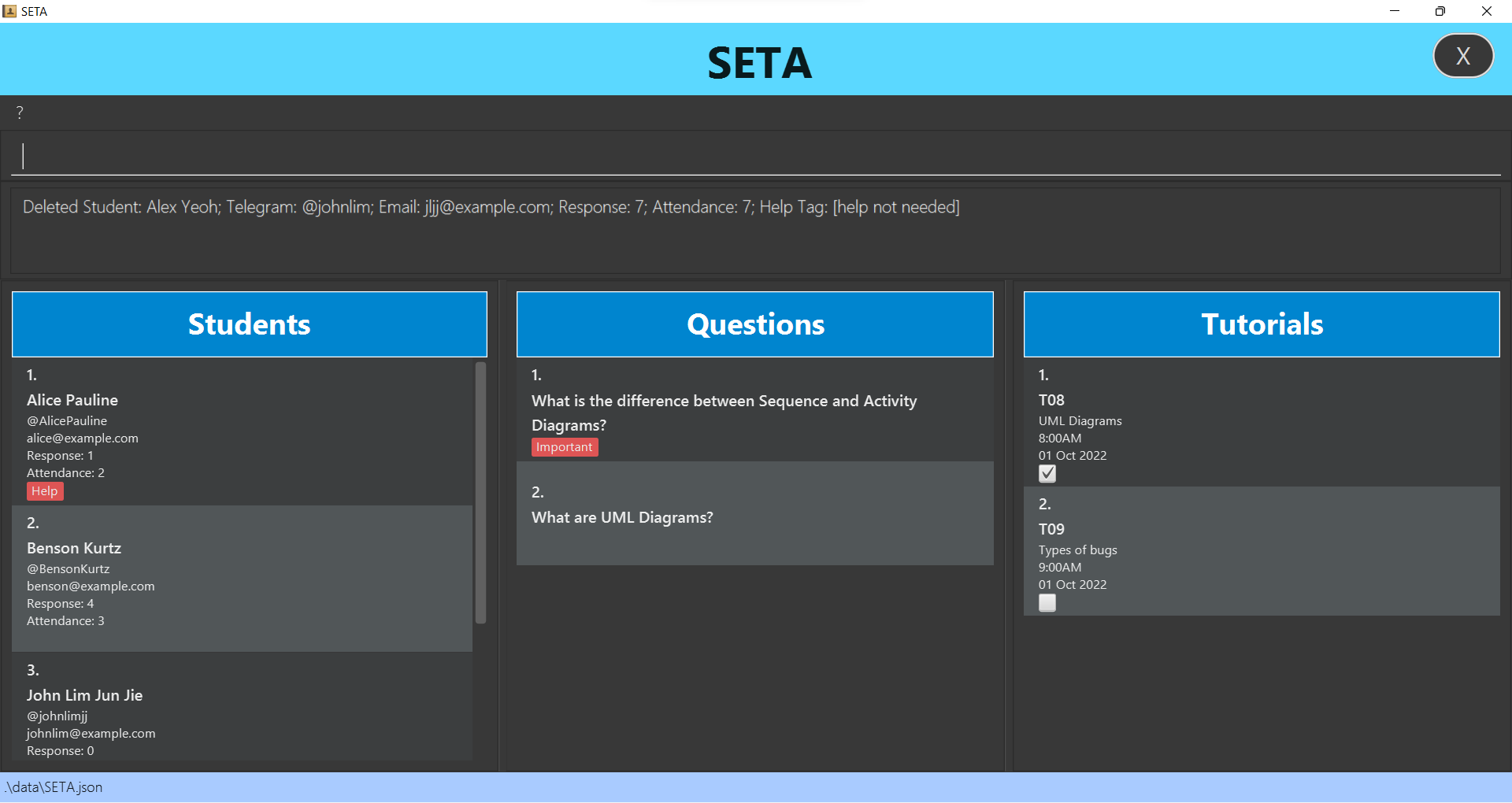
Removes a specific student.
Format: deletestu INDEX
- Deletes the student at the specified INDEX.
- The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed student list.
- The index must be a positive integer 1, 2. 3…
Example:
deletestu 1
Finding a student: findstu
Finds one or more specific students.
Format: findstu KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]
- Finds student(s) with specified KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS] in their name(s).
- The keyword is case-insensitive.
Examples:
findstu john maryfindstu john
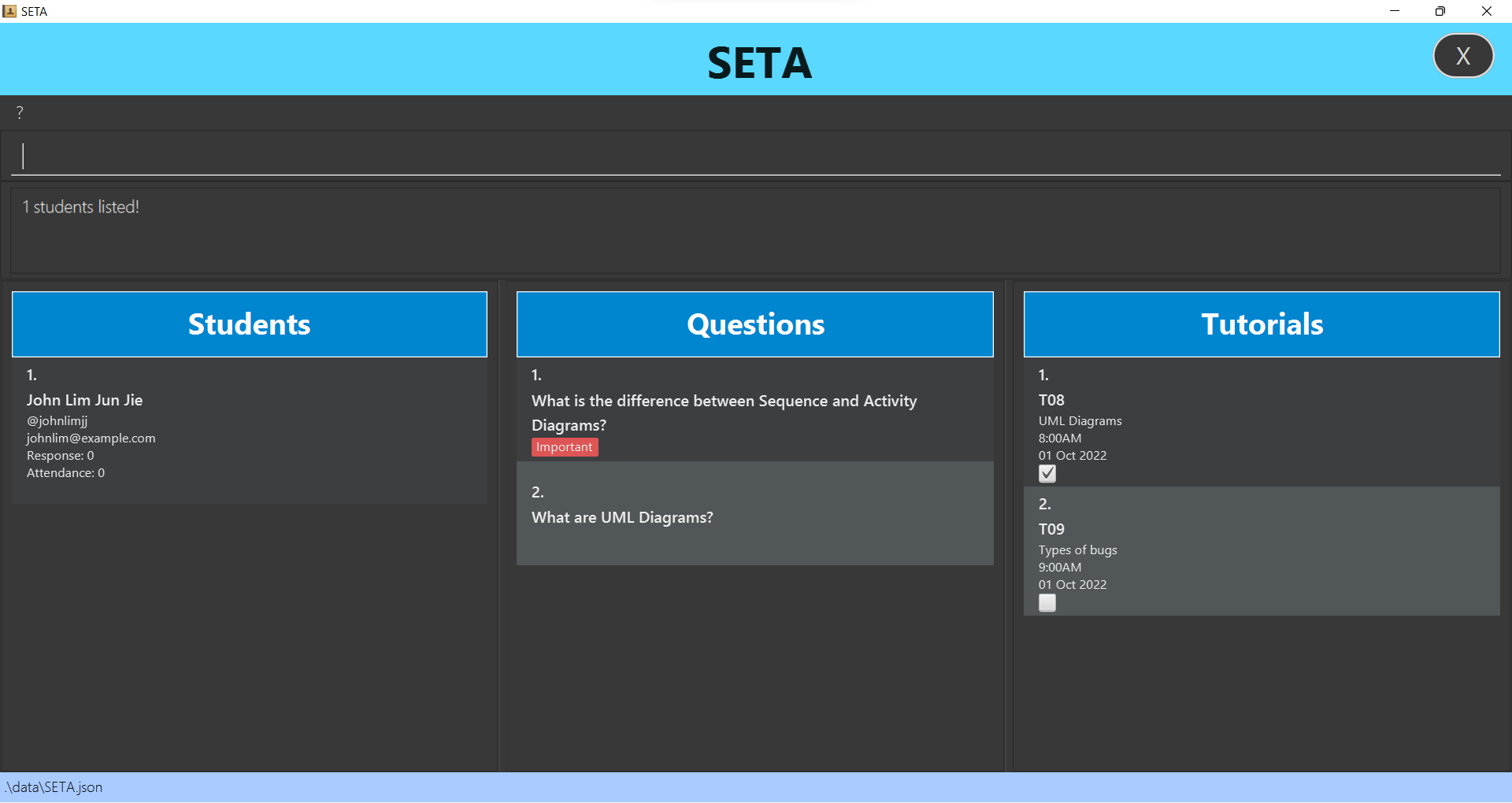
Listing all students: liststu
Lists all students in the student list.
Format: liststu
- Lists all students after student list is filtered upon finding a student or students.
Example:
liststu
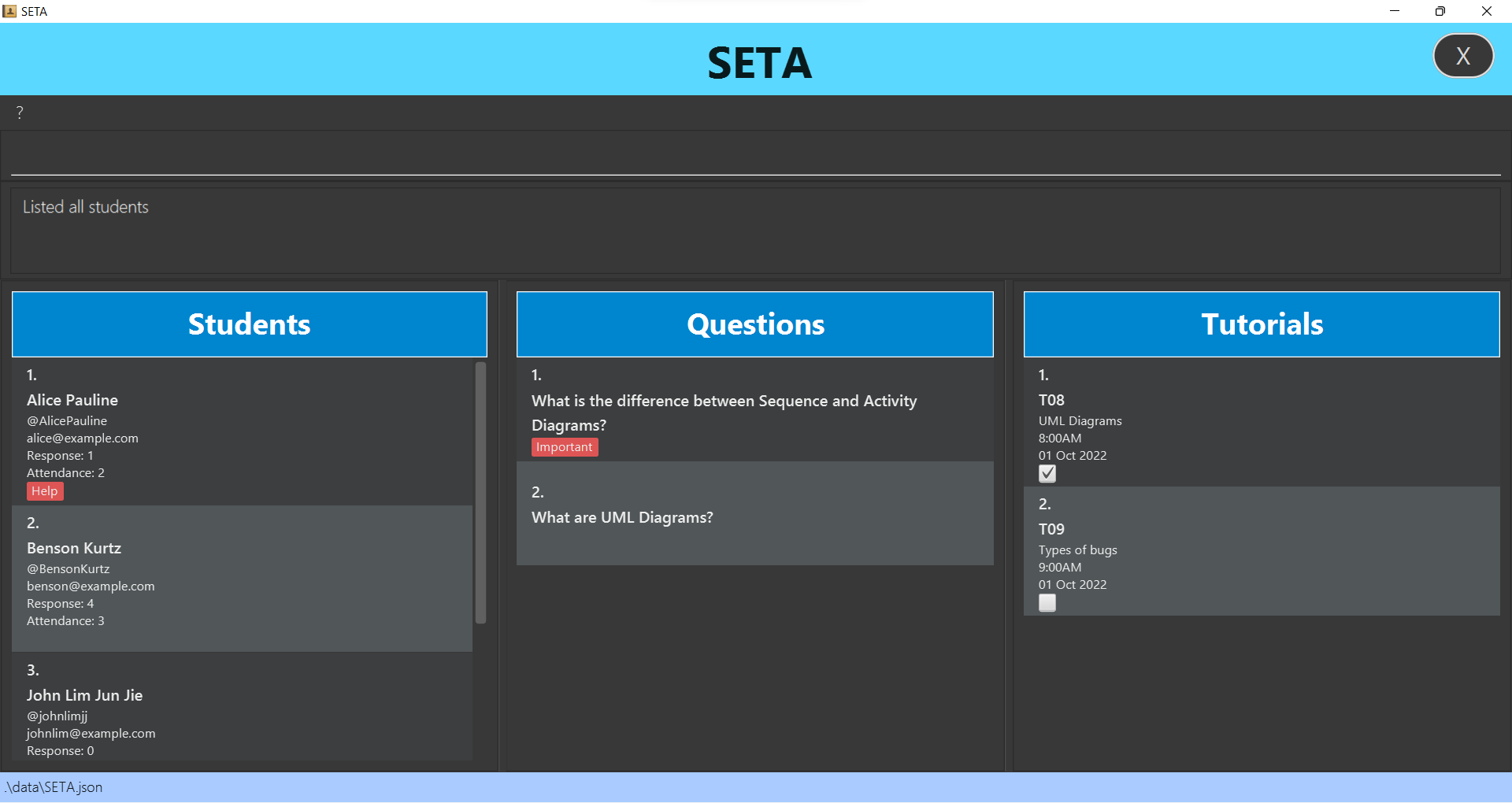
Questions
Sometimes, you may receive questions that you may not have the answer to or you may not have enough time to answer all of them during the tutorial. SETA allows you to track these questions. Furthermore, if you find a question that requires urgent clarification or critical thinking, you can indicate on the user interface that these questions are important. For questions requiring critical thinking, it would be also good to share them with other TAs so that the rest of the module’s students can benefit from knowing this question.
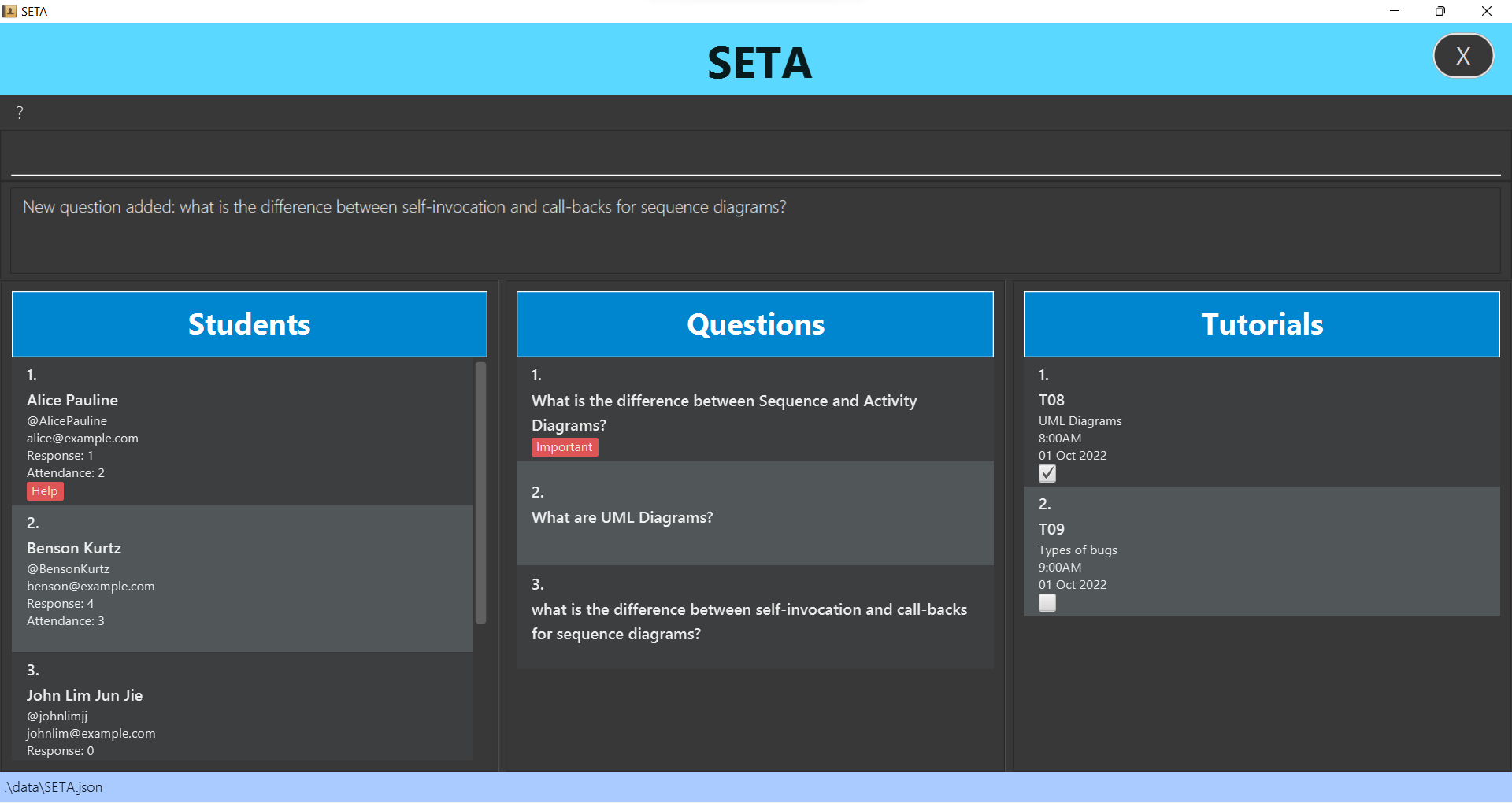
Adding a question : addq
Adds a question to the question list.
Format: addq QUESTION_DESCRIPTION
Example:
addq what is the difference between self-invocation and call-backs for sequence diagrams?
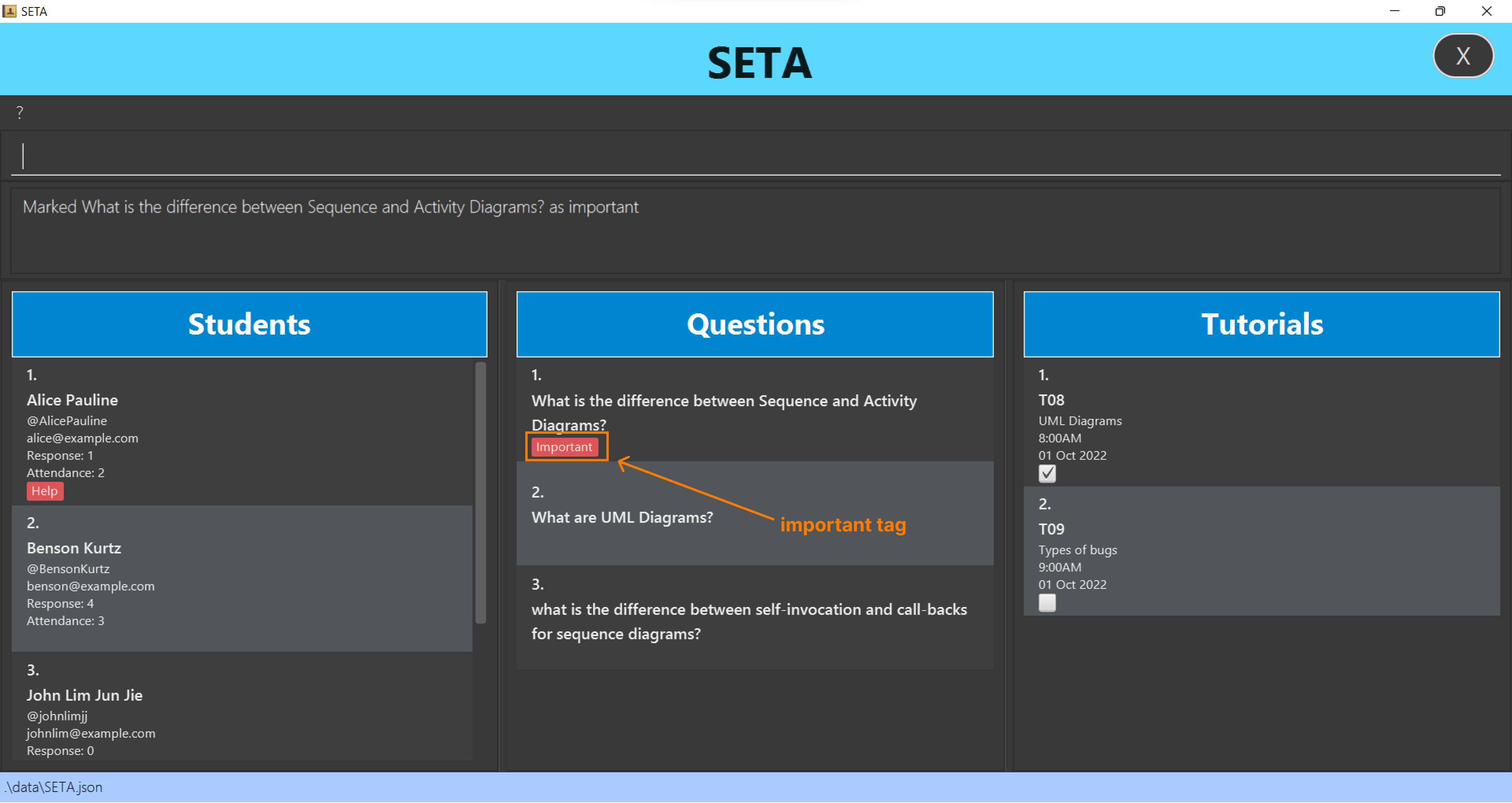
Marking a question : markq
Marks a question as important.
Format: markq INDEX
- Marks the question at the specified INDEX as important.
- The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed question list.
- The index must be a positive integer 1, 2, 3…
- The index must be within the number of questions in the question list (E.g. There are 4 questions. The possible indexes are 1, 2, 3 and 4.).
- Note: Marking a question that is already marked will not change anything.
Example:
-
markq 1marks the first question in the question list as important
Unmarking a question : unmarkq
Marks a question as unimportant. (If the question was previously or mistakenly marked as important)
Format: unmarkq INDEX
- Marks the question at the specified INDEX as unimportant.
- The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed question list.
- The index must be a positive integer 1, 2, 3…
- The index must be within the number of questions in the question list. E.g. There are 4 questions. The possible indexes are 1, 2, 3 and 4.
- Note: Unmarking a question that is already unmarked will not change anything.
Example:
-
unmarkq 1marks the first question in the question list as unimportant
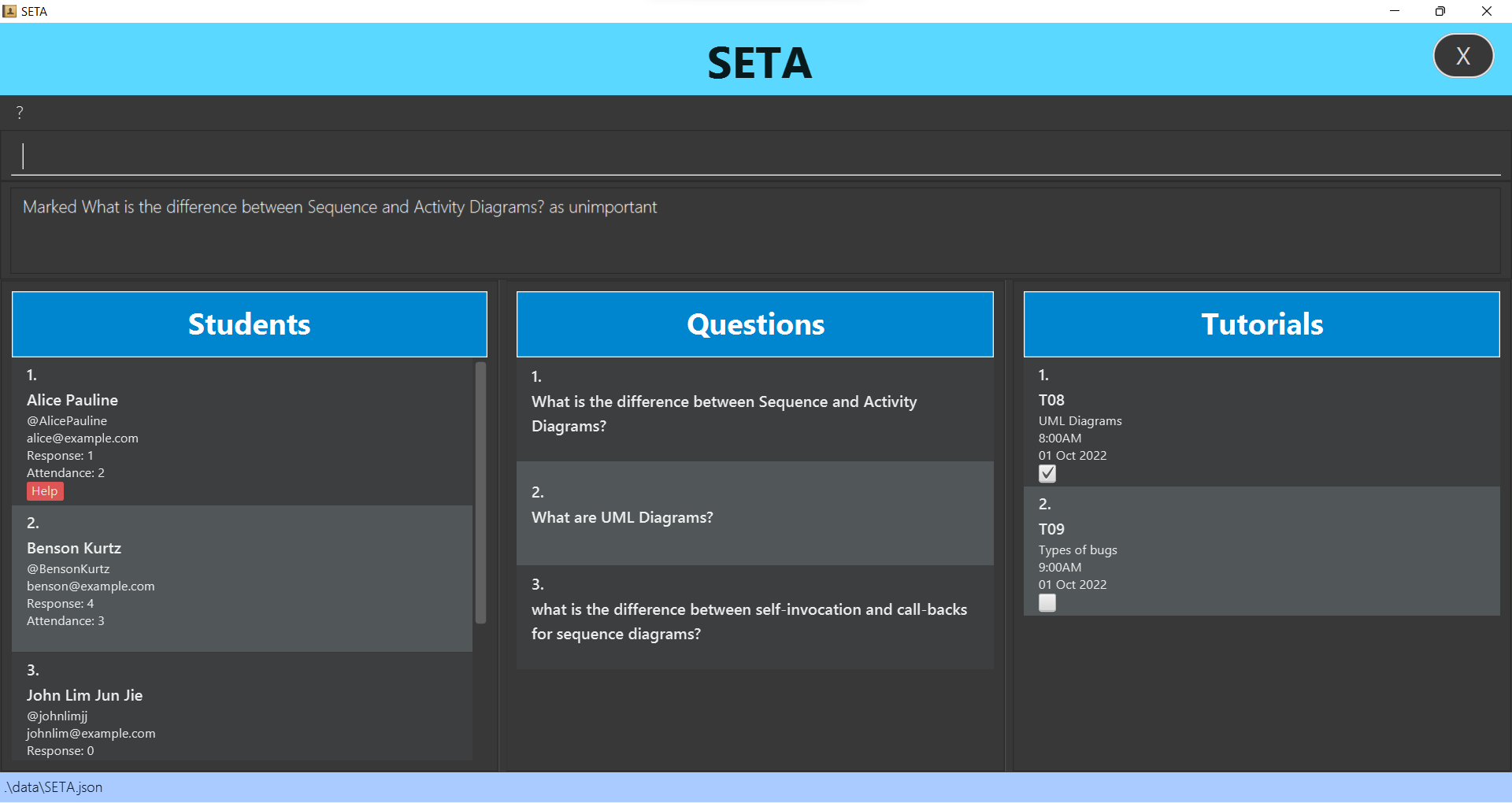
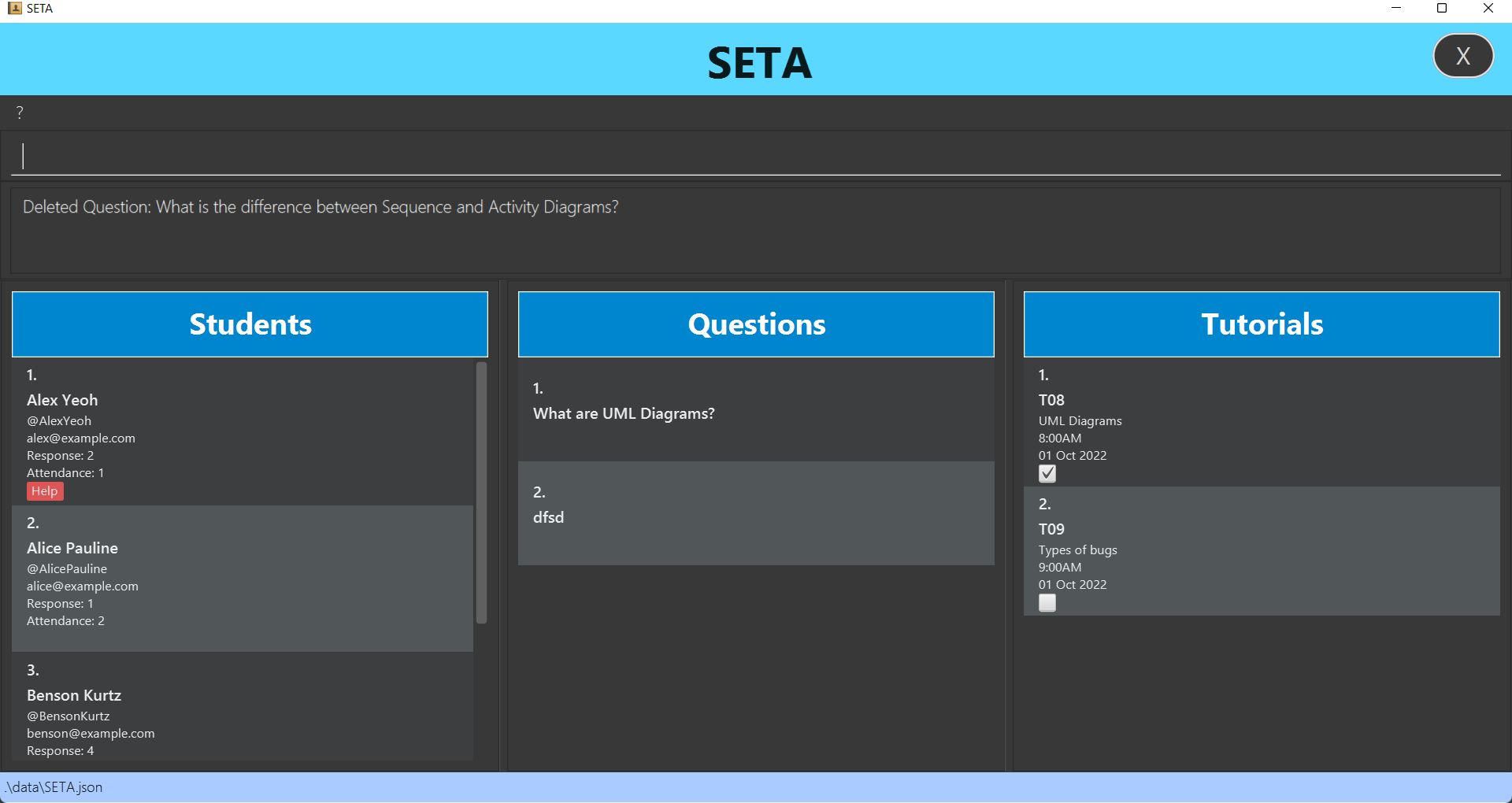
Deleting a question : deleteq
Deletes a question in the question list.
Format: deleteq INDEX
- The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed question list.
- The index must be a positive integer 1, 2, 3…
- The index must be within the number of questions in the question list. E.g. There are 4 questions. The possible indexes are 1, 2, 3 and 4.
Example:
-
deleteq 1deletes the first question from the question list
Tutorials
Each tutorial has a group number, a topic to focus on and a date and time. These correspond to the GROUP_NUMBER,
CONTENT and DATE TIME parameters accordingly.
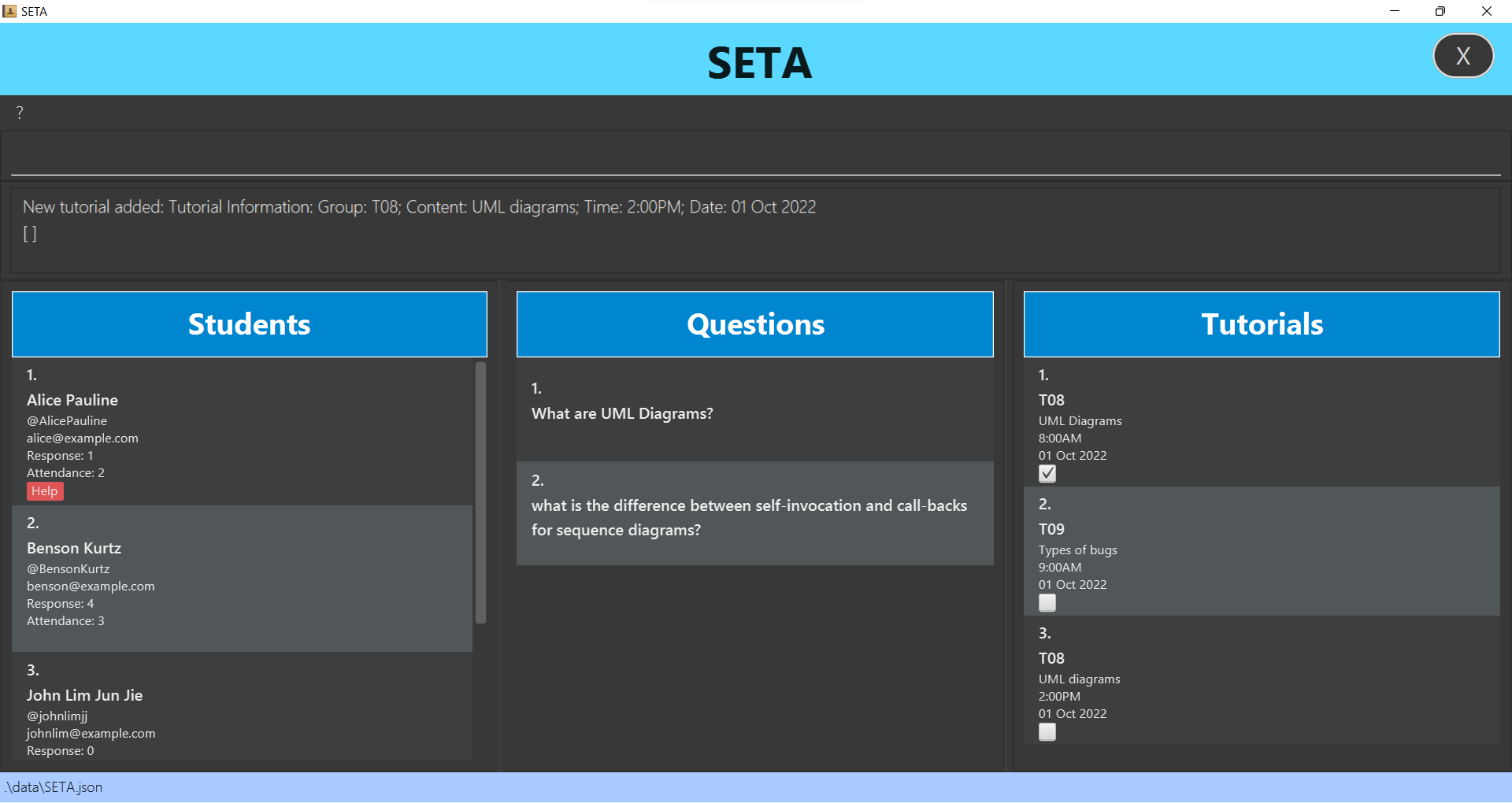
Adding a tutorial : addtut
Adds a tutorial to the tutorial list.
Format: addtut g/GROUP_NUMBER c/CONTENT t/DATE TIME
- The format of the date must be
YYYY-MM-DD. - The format of the time must be in 24h format without semicolon:
HHmm(E.g.0120,1830). - Special cases for
DATE:- Input:
2022-02-29,2022-02-30and2022-02-31 - Shown:
28 Feb 2022
- Input:
Example:
addtut g/T08 c/UML diagrams t/2022-10-01 1400
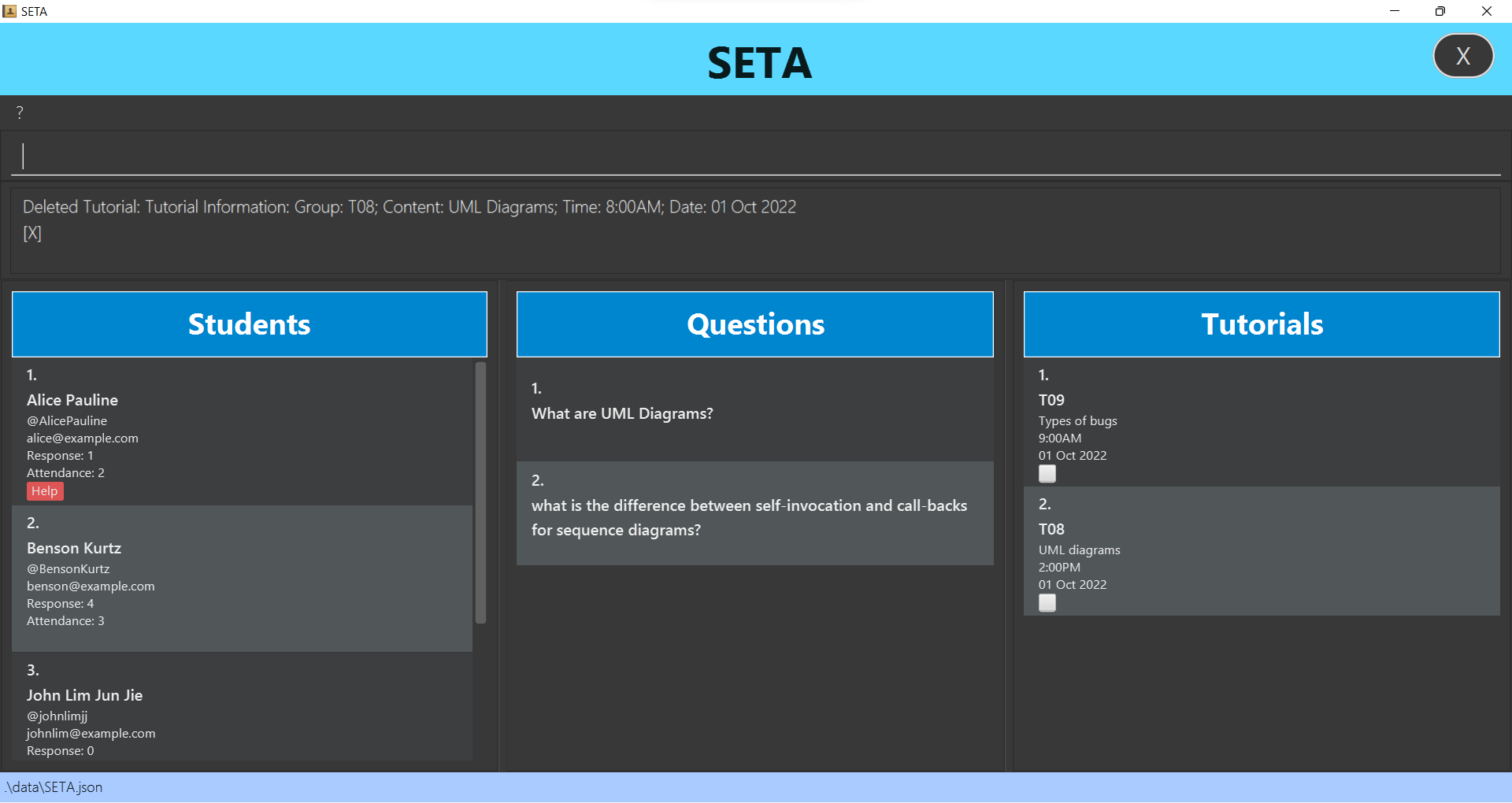
Deleting a tutorial : deletetut
Deletes a tutorial in the tutorial list.
Format: deletetut INDEX
- Deletes the tutorial at the specified INDEX.
- The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed tutorial list.
- The index must be a positive integer 1, 2. 3…
Example:
-
deletetut 1deletes the first tutorial from the tutorial list
Marking a tutorial: marktut
Marks content in the tutorial as done.
Format: marktut INDEX
- Marks the tutorial at the specified
INDEX. - The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed tutorial list.
- The index must be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, … .
Example:
-
marktut 1marks the first tutorial from the tutorial list as done.
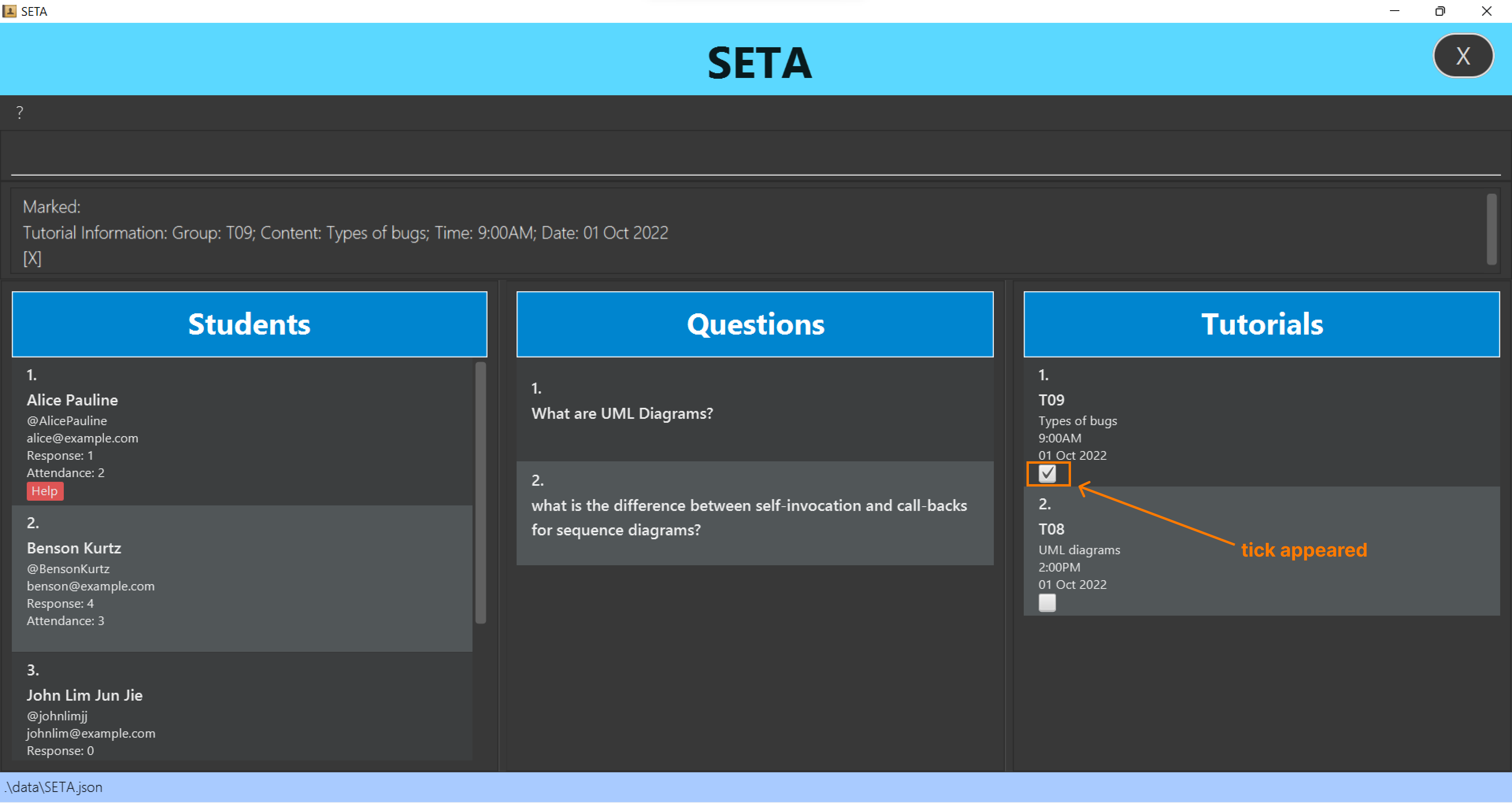
Unmarking a tutorial: unmarktut
Marks content in the tutorial as undone.
Format: unmarktut INDEX
- Unmarks the tutorial at the specified
INDEX. - The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed tutorial list.
- The index must be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, …
Example:
-
unmarktut 1marks the first tutorial from the tutorial list as undone.
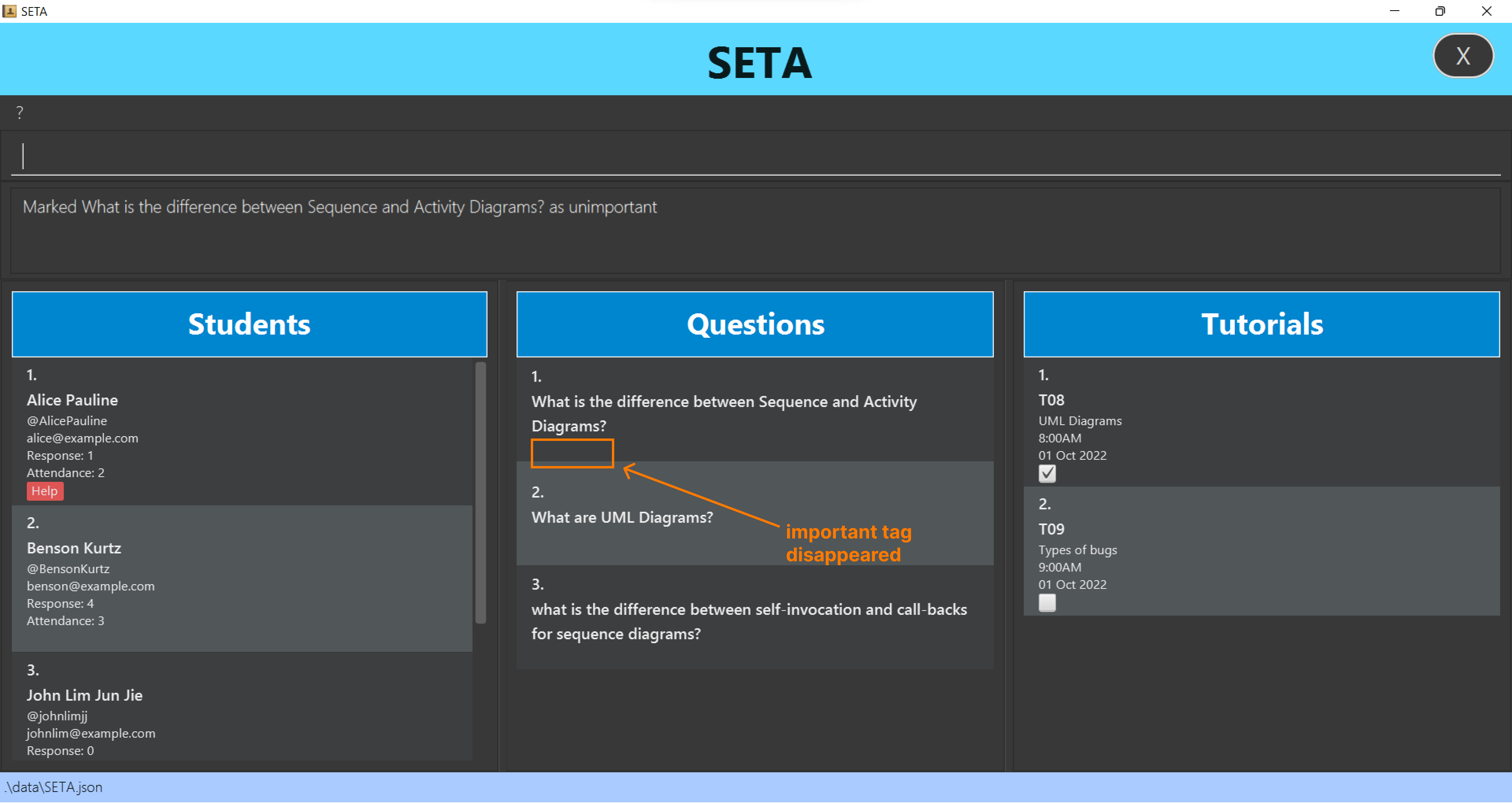
Clearing all entries: clear
Clears all entries.
Format: clear
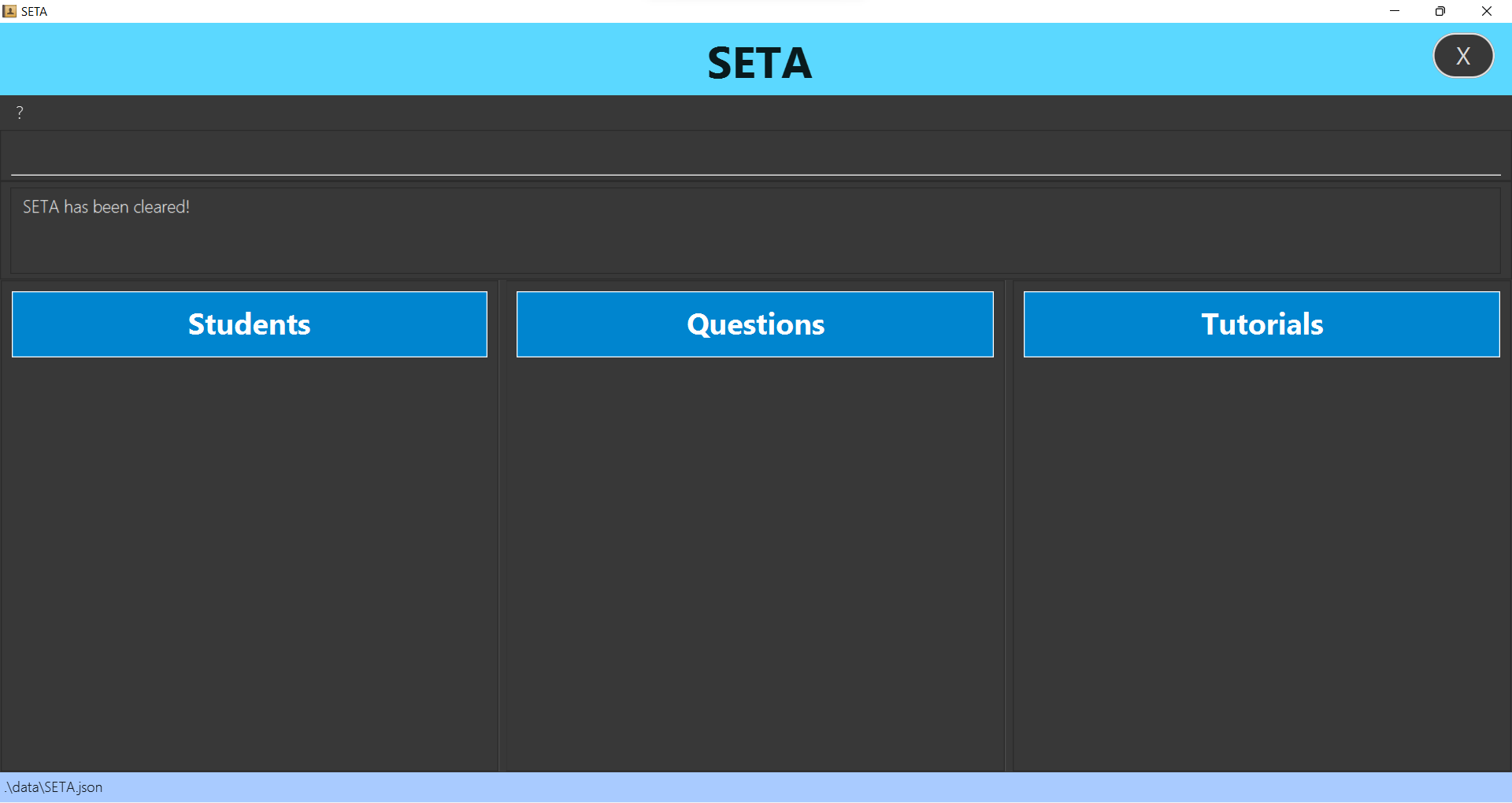
Exiting the program : exit
Exits the program.
Format: exit
Saving the data
SETA data are saved in the hard disk automatically after any command that changes the data. There is no need to save manually.
Editing the data file
SETA data are saved as a JSON file [JAR file location]/data/SETA.json. Advanced users are welcome to update data
directly by editing that data file.
FAQ
Q: How do I transfer my data to another Computer?
A: Install the app in the other computer and overwrite the empty data file it creates with the file that contains
the data of your previous SETA home folder.
Command Summary
| Action | Format, Examples |
|---|---|
| Add |
addstu, addq, addtut
|
| Attendance |
attendance, addresponse
|
| Delete |
deletestu, deleteq, deletetut
|
| Edit | editstu |
| Find | findstu |
| List | liststu |
| Mark |
markq, unmarkq, marktut, unmarktut
|
| Tag |
helpstu, unhelpstu
|
| Clear | clear |
| Exit | exit |